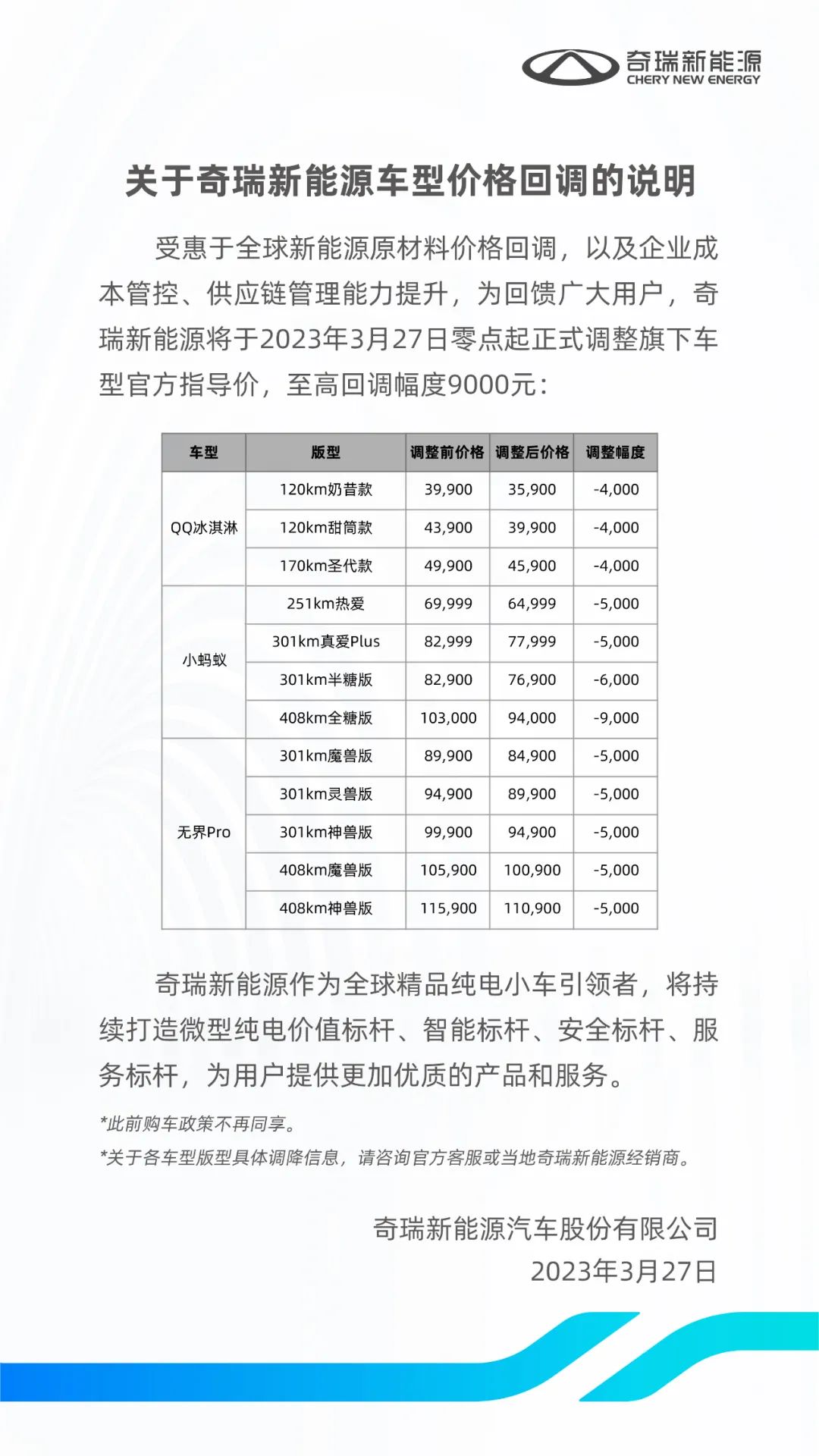
In addition to Weibo, there is also WeChat
Please pay attention

WeChat public account
AutoBeta


2024-11-17 Update From: AutoBeta autobeta NAV: AutoBeta > News >
Share
AutoBeta(AutoBeta.net)03/18 Report--
The epidemic, lack of cores and rising prices of raw materials have seriously restricted the production and sales of global auto companies. However, it never rains but it pours. A 7.4-magnitude earthquake struck near Fukushima prefecture at 22:36 (Beijing time) on March 16. After the earthquake, the Tohoku Shinkansen derailed and a large-scale power outage occurred in the Tepco area. According to the Japan Meteorological Agency, there is expected to be a tsunami risk of up to 1 meter.

Affected by the earthquake, Toyota said it would suspend production at 11 factories and 18 production lines from Monday to Wednesday, according to a new report from Bloomberg. In addition, Subaru also said that production at three factories in Gunma County will be suspended today and March 21.

Nissan China official said, "We immediately stopped the night shift at the Iwaki factory, and all the employees of the factory have been safely evacuated." At present, the production and operation of the company's Iwaki plant, Yokohama factory, Tomohama plant, Nissan technology center and Yokohama headquarters have not been damaged or affected. We will continue to pay attention to the impact of the earthquake and the safety of our employees. "
In addition to carmakers, parts suppliers are also affected. Japanese auto parts maker Denso's plant in Fukushima has also suffered equipment damage and is assessing the impact of the earthquake on production. Renesa Electronics, the world's third-largest manufacturer of automotive chips, announced that its three factories in Japan had also suspended production because of the earthquake. The three factories, NAKA, Takazaki and Mizawa, are all near the earthquake-stricken area. During the earthquake, the two factories lost power overnight, but the power supply has now been restored. As of press time, Renesas has not yet decided on the resumption of production at the NAKA and Takasaki plants, while some of the test lines at the Mize plant have resumed partial production.

As we all know, Japan is the third largest car market in the world, after China and the United States. Toyota won the top spot in global car sales with 10.5 million vehicles in 2021, while Nissan, Honda and other car companies also ranked first in the global car market. In addition, Renesas Electronics is the world's third largest supplier of automotive chips, and Denso is also a world-renowned parts manufacturer. Therefore, whether it is automobile manufacturing, parts manufacturing or semiconductor manufacturing, the Japanese automobile industry plays an important role in the world.
Researchers and professionals from the China Seismological Network Center said that 85% of the world's major earthquakes occur in the circum-Pacific seismic belt, while Japan and its eastern coastal areas belong to the circum-Pacific seismic belt, so the level of seismicity in this region is relatively high. For Japan, the 7.4 magnitude earthquake should be a relatively normal activity. On a long-term average, one or two earthquakes of magnitude 7 or above occur in Japan and its coastal areas every year.
So what is the impact of the earthquake on Japan's auto industry?
On March 11, 2011, a magnitude 9.0 earthquake struck the Pacific Ocean in northeastern Japan, the strongest ever in Asia. The huge tsunami caused devastating damage to Iwate, Miyagi and Fukushima prefectures in northeastern Japan and triggered a nuclear leak at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. At that time, Toyota suspended production at 12 factories for three days, Nissan stopped production at five major factories in Fukushima, Tochigi, Yokohama, Tomohama and Shizuoka, and Honda's research and parts factories in Tochigi Prefecture were closed due to damage. due to difficulties in the supply of spare parts, four major vehicle factories in Saitama Prefecture and Shizuoka Prefecture have stopped production.
On April 14, 2016, a 6.2 magnitude earthquake struck Kumamoto Prefecture, Japan. Affected by the earthquake, Toyota. Honda, Nissan and other car companies announced a temporary suspension of production. Among them, Toyota's Japanese production line suffered a massive shutdown for nearly a week because of a broken supply chain. On September 6, 2018, a magnitude 6.7 earthquake struck Hokkaido, Japan. Toyota said it had suspended production at 16 of its 18 final assembly plants since Sept. 8 due to supply chain disruptions, with its plant in Komura, Hokkaido, the hardest hit, which mainly produces AT, CVT gearboxes and gearboxes.
On February 1, 2021, another 7.3-magnitude earthquake struck near Fukushima, Japan, triggering a massive power outage and disrupting the supply of auto parts in Japan, which had an impact on Japan's semiconductor and auto industry. After the earthquake, Japanese semiconductor giant Renesa Electronics announced that production at its Nake plant was affected by a power outage and suspended production for safety reasons and is expected to return to pre-earthquake production capacity within a week. Toyota announced that 14 production lines at nine factories in Japan will be temporarily suspended from 17 to 20, with a maximum of 4 days. In addition, Nissan's Fukuoka plant was also affected by the earthquake.

Judging from the above cases, the impact of the Japanese earthquake on the Japanese auto industry is not very great, even if the "311" earthquake in Japan triggered a huge tsunami, Toyota only stopped production for three days. Compared with the earthquake, the current supply of parts and semiconductors is the main factor restricting the development of Japanese car companies. Toyota said it suspended domestic production in March because of a shortage of semiconductors and would suspend production at a factory for eight working days from March 22 to the end of the month. Toyota recently said it would cut domestic production by as much as 20 per cent in April, May and June to ease pressure on suppliers due to shortages of chips and other components. In addition, according to the latest disclosure of Toyota, due to the impact of semiconductor chips and the epidemic, it expects to stop production at seven production lines at five factories in Japan in April, and global production is expected to be about 750000 in March (250000 at home and 500000 overseas). However, despite a reduction in its production target, Toyota will maintain its production target of 8.5 million vehicles this year.

The major impact of the earthquake is Renesa Electronics. As a global manufacturer of automotive specification-grade chips, Renesa Electronics controls nearly 1/3 of the global market share of automotive microcontroller chips, while the Nake factory accounts for 2% of all the company's semiconductor production equipment. The chip products of the factory 2max 3 belong to automotive chips, and the current global core shortage is serious. The shutdown at the Renesas electronics plant will once again exacerbate the impact on the production of local and global carmakers.

Global chip shortages have plagued companies from smartphone makers to consumer electronics companies and carmakers, forcing companies, including Toyota, to cut production again and again. At the end of February, Toyota suspended production at all its factories in Japan for a day after a cyber attack on its suppliers. The Japanese giant is going through an ill-fated year.
Welcome to subscribe to the WeChat public account "Automotive Industry Focus" to get the first-hand insider information on the automotive industry and talk about things in the automotive circle. Welcome to break the news! WeChat ID autoWechat
Views: 0
*The comments in the above article only represent the author's personal views and do not represent the views and positions of this website. If you have more insights, please feel free to contribute and share.










© 2024 AutoBeta.Net Tiger Media Company. All rights reserved.