In addition to Weibo, there is also WeChat
Please pay attention

WeChat public account
AutoBeta


2024-11-17 Update From: AutoBeta autobeta NAV: AutoBeta > News >
Share
AutoBeta(AutoBeta.net)04/19 Report--
Affected by the spread of COVID-19 's epidemic and instability of the supply chain, Toyota's nine factories and 10 production lines in Japan will face varying degrees of shutdown in May this year. Toyota announced on its website that it will stop production for several days in May at a number of factories in Japan, including the Takaoka plant in Toyota City, Aichi Prefecture, and the Takahara plant in Takahara City, Aichi Prefecture, a total of 10 production lines, involving vehicles including Corolla, C-HR, RAV4 and Lexus LS, IS, RC, NX, CT, UX, etc. According to news released by Toyota, the longest shutdown time of the nine plants is Line 1 at the Miyada plant in Kyushu and Line 2 at the Fujimatsu body plant, both of which have been shut down for six days. The shortest shutdown time is the No. 3 production line at the Tanahara plant, which only stops production for one day.
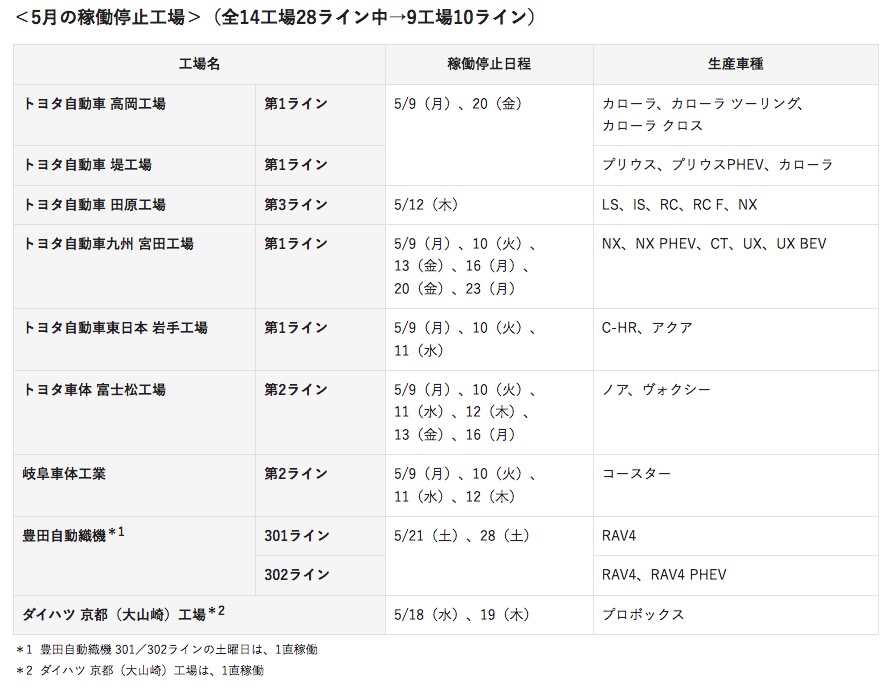
In view of this, Toyota also officially announced that it will cut global production by 10% to 750000 vehicles in May, of which Toyota's domestic production in Japan will fall to 200000 vehicles and overseas market production will fall to 550000 vehicles. Toyota said the drop in production was mainly due to the COVID-19 epidemic and semiconductor shortages.

As a result, the average monthly production from May to July this year is about 800000 vehicles, in other words, Toyota is expected to produce about 240 vehicles from May to July 2022. In this regard, Toyota stressed that due to the COVID-19 epidemic and semiconductor shortage, the next few months of production is difficult to predict.
On March 11 this year, a spokesman for Toyota of Japan said that Toyota plans to cut production capacity in Japan's domestic market by 20% within three months from April. To ease the pressure on suppliers caused by shortages of chips and other parts. Toyota's new production plan for the April-June period in 2022 was cut from 2.8 million to 2.5 million, a decrease of about 300000 compared with the original plan, but an increase of about 10 per cent from a year earlier (2.26 million in April-June 2021), of which it fell by about 10 per cent to 100000 in May. After another adjustment, Toyota's global production will be reduced to 750000 vehicles in May. So far, it is not known whether the suspension of production at a number of local Japanese factories in May will affect Toyota's sales in fiscal year 2022.

From January to February this year, Toyota produced 1371887 vehicles worldwide and sold 1453494 vehicles worldwide, according to Toyota Motor Group data. Of these, Toyota produced 740996 vehicles worldwide in February, including 253258 in Japan's domestic market, up 4 per cent from a year earlier, and 487738 in overseas markets, up 15 per cent from a year earlier.
In addition to Toyota, the production problems of many Japanese car companies are also in a serious state because of the disruption of the supply chain of some auto parts caused by the spread of COVID-19 epidemic.
On April 15, Mazda officially released news that, affected by the closure and control of the COVID-19 epidemic in Shanghai, the factories of Mazda's cooperative enterprises stopped production and interrupted the supply of some spare parts. Mazda's Hiroshima headquarters factory and Fangfu factory in Japan will stop production for four days from the 21st to the 26th. In addition, in addition to the suspension of production at the Mazda joint venture plant, logistics such as sea and air transportation are also expected to be delayed. In fact, prior to this, two Mazda factories in Japan have announced the suspension of production twice this month. Together with the suspension of production from the 21st to the 26th mentioned this time, Mazda's domestic factories will stop production for a total of eight days this month.

Prior to this, two Mazda plants in Japan stopped production on April 4, April 5, April 14 and April 15, and on March 24, Mazda announced that its Hiroshima and Fangfu plants in Japan would stop production for two days from April 4 to 5. On April 12, Mazda said that due to the closure and control of the epidemic, the factories of Mazda's joint ventures stopped production and some parts could not be procured. Mazda's Hiroshima headquarters factory and Fangfu factory in Japan will stop production for two days from April 14 to 15. According to previous reports of auto industry concern, Mazda's two factories are located in the southern district of Hiroshima City, Hiroshima Prefecture (Hiroshima Corporation factory) and Fangfu City, Yamaguchi Prefecture (Fangfu Factory). Judging from the reasons for the above three stops, Mazda stopped production three times this month, all due to the interruption of logistics and a shortage of auto parts due to the spread of the COVID-19 epidemic. At present, Mazda did not disclose whether the suspension of production at the two plants on the 8th of this month will affect its subsequent production.
On April 7, Honda announced that due to the spread of the epidemic and parts shortage and other factors, Honda Japan's main plant expanded to reduce production in April, of which, Suzuki factory in Sanchong prefecture will reduce production by about 30%, and Saitama plant in Saitama prefecture will reduce production by about 10%. After the April cut, compared with the previous plan made in February, the scale of the reduction reached 30%.
On April 5, Mitsubishi Motors said that the supply of spare parts was interrupted due to the COVID-19 epidemic and the closure management in Shanghai (the Shanghai factory is a supplier of some Mitsubishi automobile parts). The production line of Mitsubishi Motors' main Japanese plant Okazaki (Okazaki City, Aichi Prefecture) will be suspended from April 11 to 15 for a total of five days.

In fact, since 2021, due to the slow supply of spare parts and the long-term lack of relief from the chip shortage under the epidemic, a number of Japanese car companies have announced production suspensions or production cuts, including Mazda, Mitsubishi Motor, Honda and so on. New car sales in Japan in the 2021 fiscal year to the end of March were 4.21 million, the lowest in 45 years, according to the latest figures. Of Japan's eight major car companies, with the exception of Mitsubishi, the other seven showed a decline in sales, with Toyota down 9% and Mazda down 16%, the highest decline among Japan's eight car companies.

Public data show that new car sales in Japan have shown negative year-on-year growth for three consecutive years. Japan's National Federation of Light Automobile Associations said that in addition to the shortage of semiconductors, the epidemic in Southeast Asia has led to stagnant procurement of spare parts. the factories of manufacturers have to stop production or reduce production, which also affects the sales of new cars. It also said: "with the shortage of semiconductors and the continued stagnation in the procurement of components from overseas, it is difficult to predict how long the impact on new car sales will last." "We do not expect the shortage of chips to be resolved soon and may continue into the next fiscal year," Toyota said when it announced its results in February. "
Industry analysts pointed out that the supply chain of Japan's automobile industry is not only affected by the epidemic, but also by the high prices of many kinds of electric vehicle raw materials caused by the conflict between Russia and Ukraine. In fact, the entire automotive industry is facing rising raw material prices, tight parts supply chain and chip shortage. In addition to Japanese auto companies deeply affected by the short-term impact of chips, Volkswagen Group CFO Arno Antlitz has previously said that it is expected that chips will still be in an imbalance between supply and demand by 2024. Chipze, chairman of BMW Group, said the semiconductor shortage in the automotive industry could last until 2023. "We are still at the peak of the chip shortage and are expected to see an improvement next year, but the chip shortage will not be fundamentally solved until 2023," he said.
As of April 17, the global auto market has lost about 1.498 million vehicles this year, according to AFS. Among them, the production reduction in the Chinese car market reached 92000, accounting for 6.1 per cent of the cumulative production reduction in the global car market. AFS expects global car production cuts to climb to 2.2498 million this year, with nearly half of them in Europe, nearly 1/4 in North America and 197200 in China.
Welcome to subscribe to the WeChat public account "Automotive Industry Focus" to get the first-hand insider information on the automotive industry and talk about things in the automotive circle. Welcome to break the news! WeChat ID autoWechat
Views: 0
*The comments in the above article only represent the author's personal views and do not represent the views and positions of this website. If you have more insights, please feel free to contribute and share.











© 2024 AutoBeta.Net Tiger Media Company. All rights reserved.